Hip joint arthritis (mockery)- It is a chronic degenerative disease of the joints, which leads to bone tissue deformation.With Coksarrosis, all the components of the joint are involved in the pathological process: articular cartilage, bone structures next to the cartilage, articular shell, ligaments, capsule and adjacent muscles.In the event of illness, the articular cartilage is destroyed, micro-red bones and bone (bone growth) occur and an inflammation of the muscle-tempo-sheets of the hip joint occur.
In the world, every fifth person complains of common problems with the joints.This can be so much pain or restriction of joint movement and a combination of these symptoms.Every second vision of external patients is reduced in patients with bone disorders, while 66 % of cases are under 65 years of age.According to the latest epidemiological study, the prevalence of knee and hip joints between the adult population is 13 %.
Risk Factors for the Development of Coroxaris:
- Genetic predisposition.A common cause of hip joints is the congenital or obtained mutation of type II Prollagen.
- Elderly age.The possible cause of the prevalence of articulation in aging is a deviation between the survival of the level in the common cartilage of the external environment and its capabilities for rehabilitation.
- Floor.Women suffer from osteoarthritis more often than men.This is due to the effects of the effect of female sexual hormones of estrogen on bone metabolism.However, the influence of the floor is ambiguous - according to some authors, as opposed to lesions on other joints, there are no differences in the sexual base for Coksarrosis: in men, hip arthritis is as often as in women.
- Excessive body weight.The relationship is demonstrated between excessive body mass and the appearance of articles.Excessive adhesive tissue increases the harmful load on cartilage.In addition, the adipose tissue produces a pro -inflammatory enzymes that harm the cartilage tissue.
- Frequent growth of bones and joints.According to studies, 80 % of the corrosion, which occurs for no obvious reason, is associated with previously unacceptable defects in the development of hip malformation and underwriting malformation.
- Heavy physical work.An excessive load on hip joints with certain types of physical work can lead to damage to the joints and arthritis formation.In danger are agricultural workers, excavators and people with similar work specialties.
- Injuries.The risk of developing the carxar is increased after an injury to the hip joint.In addition, both injured both may participate in the process.
- Professional sports game.Professional sport can cause the appearance of koroxaris both because of excessive joint loads and injuries.Probably dangerous sports include heavy sports, sports jumping, parachute sport.
- Bones and common diseases- Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, joints, vascular necrosis, tail arthritis, etc.
- Endocrine pathologies- Hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, acromegaly (reduced function of the anterior pituitary), diabetes, obesity.
If similar symptoms are identified, consult a doctor.Don't self -healing - it's dangerous to your health!
Symptoms of hip joints
The main symptoms of the consensus include: pain, mobility restrictions and joint crisis, distortion, functional lower extremity reduction and periodic joint swelling.
Pain of various intensity.The pain in the joint is initially insignificant and occurs for a short time.They appear or intensify during walking or with other physical activity, for example, during occupations, inclinations and weight lifting.As the disease develops, the pain is intensified and even a long rest does not bring relief.In addition, the pain occurs with prolonged stillness and stabilization of the joint in one position.
Patients complain about SO -Called "starting" pain in the hip joints after sleeping, leading to a car and other prolonged stillness."Starting" the pain for koroxari does not last more than 30 minutes.The pain is intensified during hypothermia or in a stressful state.They can be detected in the glut or groin area, on the front or lateral surface of the thigh.By spreading the pain over the nerves of the lumbar grid, it can be transmitted to the thighs that are removed from the center of the body or the knee.Sometimes the pain applies to the lumbar spine and tail.
Limiting the mobility of the joints.The movements in the hip joint with coksarrosis are limited due to the pain.At the same time, rotation (turns both inside and out) and bringing the lower extremity (moving in the body) is more frequently disturbed, but may be limited (movement from the middle axis of the body), as well as bending and extension.The inability to make passive movements in the joint due to a severe pain syndrome causes compensatory pelvic prejudice.The patient's gait changes, the buttocks come back, the body deviates forward when it carries the weight to the damaged side.With bilateral damage to patients with coksarrosis, a "duck walk" is formed.
With the periodic appearance of the carxarisswelling in the jointwhich can be invisible because of the layer of muscle and fat.Also the disease is typicalCrystal in the joints during movement, gradual distortion and functional reduction in the lower extremity.
Often, a joint is affected by the disease, then the procedure applies to others.But sometimes articulation affects several joints at the same time and multi -thexialritis occurs.Multihurus is characteristic of the elderly or with hereditary predisposition and at the same time diseases - diseases of bone, joints and endocrine disorders.
Pathogenesis of hip joints
In the pathogenesis of hip joint articles, an important role is played by mechanical damage (injuries and minor injuries due to increased physical activity in the joint) and genetic, hormonal and metabolic factors.It is often not possible to determine which factor has affected the development of the disease in a particular patient, but often the disease develops after damage to the tissue with mechanical injury.
Damage to the tissue stimulates the division of cartilage cells (chondrocytes), while the production of pre -inflammatory cytokines is increased, which usually exist in cartilage only in small quantities.Cytokines launch the inflammatory process, for example, under the influence of pre-inflammatory IL-1 pre-inflammatory cytokine, the enzymes that destroy the cartilage of the joint are distinguished.Also, under the influence of cytokines, the production of the TSOG-2 enzyme and other substances that have a toxic effect on cartilage is increased.
The articles also play an important role in the development of groxhar - inflammatory diseases of the articular shell of the joints or joints by accumulation of fluid in the cavity.
Decrease in elasticity and resistance of the synovial cartilage associated with metabolic disorders leads to a decrease in its resistance to mechanical stress.With Coksarrosis, all components of the joints are involved in the pathological process, including a substrate bone.Due to the fact that the large joints of the lower extremities represent large joints of the body, they have significant mechanical pressure, due to which they occur shortly in the sub -brain plate and the cartilage.As a result of microbials, the underdent bone is compressed, which leads to the peripheral development of osteophyte tissue.And this, in turn, stimulates further degradation of the articular cartilage.
In some cases, arthritis of the hip joint is inherited.Hereditary arthritis is assumed to be a polygonal heritage - due to the action of many genes, each of which is weakly affected.The cause of certain diseases is a mutation in genes that codify macromolecules of the articular cartilage, which causes its ruptures.The genes responsible for the division of coarse cells can also suffer.In addition, metabolic disorders, such as pyrophosphate arthropathy, are inherited - a disease in which calcium pyrophosphates accumulate in articular cartilage and synovial fluid.
Sorting and stages of developing hip joints
Depending on the causes of the disease, the body is divided into two main forms: primary (idiopath) and secondary (resulting from or due to other diseases).
Primary Coksarrosis:
- Localized (only hip joints affect):
- unilateral;
- bilateral.
- Generalized (multi -mixtrus) with at least three groups of joints (for example, hip, knee and small joints or legs).
Secondary arthritis:
- Post -traumatic:
- Acute - as a consequence of acute damage.
- Years - due to classes of certain sports or as a result of professional activity.
- Metabolic Diseases (Ophthalmosis, Hittomy, Wilson's Disease, Gaucher disease).
- Congenital pathologies and developmental defects (congenital hip joint dysplasia, pertes disease, femoral leveling, hyperactivity syndrome, lower extremity reduction, scoliosis, bone dysplasia).
- Endocrine pathologies (acromegaly, hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism, obesity).
- Calcium salts (pyrophosphate arthropathy, calcifying tendonitis).
- Bone and joint diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, penny disease, vascular necrosis, infections).
According to clinical manifestations, the following forms of carxar are distinguished:
- A little coincidental.
- It is manifested, manifested by bright clinical symptoms:
- Rapidly progressively, in which the symptoms develop in the first four years of the onset of the disease.
- Slowly progressively - clinical significant symptoms occur after five years of the course of the disease.
According to Figure X -Ray, two types of hip joints can be identified:
- Hypertrophic - with signs of increased recovery response (the lesions are replaced by a new tissue, for example, appear osteophytically).
- Atrophic (decrease in tissue volume).
Stages of the disease can be identified radiologically and clinically.To determine the radiological stage of the articulation of the hip joint, the classification of Kellgren and Lawrence (1957) is most commonly used.
Articulation stages in radiological classification
| Stage | Signs |
|---|---|
| 0 | There are no signs of articulation in pictures x -ray |
| 1 | Common gap does not change, are illustrated individual peripherals osteopic |
| 2 | Common gap does not change, significantly depicted peripheral osteophytes |
| 3 | The height of the joint gap is reduced moderately, depicted significantly peripheral osteophytics |
| 4 | The height of the joint gap is significantly reduced, significantly peripheral osteophytics occur and subsexal osteosclerosis (bone condensation below the lower surface of the cartilage with the structure of the cartilage) |
To determine the clinical stage of the disease, the classification (1961) is used, which uses both the clinical signs and the imaging criteria.
Clinical stages of articulation
| Stage | Signs |
|---|---|
| 0 | The synovial gap is without doubt and unevenly, the edges of the articular cracks are slightly sharp (initially osteophytically), a slight restriction of movements is noted |
| 1 | The synovial gap is significantly reduced (50-60 %), significant osteophytics, hypotherapy osteocystal and cystic enlightenment on the bone levels.The clinic is dominated by the restriction of mobility in joints, a rough crisis during moves, insignificant or moderate muscle atrophy |
| 2 | Deform, rigidity of the joint.The synovial gap is reduced by more than 60-70 % of the rule or completely absent, extensive osteophytical, sub-brain cysts, articular "mice" are depicted, cartilage or mixed pathological formations found in the hinge cavity |
Complications of hip joints
With Korotheosis, all complications are exactly associated with pathological changes in the joints.
Coksarrosis's course may be complicated by local inflammatory processes:
- Bursite - inflammation of articular bags in the joints.
- Tendovaginitis - inflammation of the inner shell of the vaginal tendon.
- Nerve tunnel syndrome due to the formation of large osteophytes or with the joint deformation.
With the evolution of the conscientious and its transition to clinical stages II and III, the pain limits the mobility of the joint and over time the hinge of ankylosis (fibrous, bone or cartilage) appears, accompanied by its complete stillness.
Significant distortion of the joint can lead toFractures or aseptic bone necrosis.For Coksarrosis, aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is the most terrible complication.
With intense coksarrosis, can happenhypoglycaemia and dislocation of the jointas well as the penetration of the femoral head into the pelvic cavity.The outbreaks and hypotension of the hip articulation lead to pain (initially acute, then dull and pain), intensifying during walking and other physical activity, as well as the joint deformation, lame and sometimes to reduce the affected end.
Despite the lack of systematic manifestations of the article itself, in modern clinical practice, more attention is given to the diseases associated with it.These are such pathological conditions that exist or arise in the context of current disease.In relation to the inflammatory reactions that arise during the articulation, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the inner walls of the vessels is enhanced, which increases the riskCardiovascular disease.Reduction of physical activity due to pain and restriction of joint mobility leads toObesity, depression and deterioration of quality of life.With prolonged use of non -sergeoidal anti -inflammatory drugs,Upper gastrointestinal sections are affected,And alsoThe risk of cardiovascular pathologies and kidneys is increasing.
Diagnosis of hip joints
The diagnosis of "coksarrosis" is made based on clinical manifestations and radiological examination.There are no characteristic laboratory signs to diagnose the articles.
Between clinical eventsThe master for the diagnosis of the articles of the hip joint is his pain and character.The pain for articulation of the hip joint occurs and develops gradually in several years (sometimes several months in a quick progressive form).Pain occurs or reinforces during physical activity or in posture.If the patient begins to feel only pain, then inflammation (arthritis) was incorporated.The statement is made up to 30 minutes in the morning and with prolonged stillness.
Limiting the mobility of the joints is gradually increasing, this is true for both active and passive movements.With the development of the disease, the joints are deformed, a functional decrease in the length of the limb may occur.
In physicin examinationThere is a restriction on the mobility of the joints, their deformation, the reduction of extremities, the pain in the joint of the joint and the high rotation of the femoral bone, the muscle atrophy.
Laboratory methodsIt is not required to diagnose the articular articular articular articles.However, they can be used to differential diagnosis of arthritis (rheumatoidal and chronic), since arthritis does not have inflammatory changes in overall blood test and rheumatoid factor and uric acid levels do not increase.In addition, they use laboratory tests, revealing contraindications for drug treatment methods.
Organic methodsTo diagnose hip joints:
- Radiography- This is the main method of diagnosing hip joint articles.Radiography determines the changes that characterize the grain: narrowing of the joint gap, osteophytes, erosion and expulsion of the cartilage, sub -brain cysts and osteosclerosis.The X -Ray test is a classic method for diagnosing the trunk and radiological points form the basis of the sorting of corst.However, at present, the methods of visualization of the joint are increasingly used, such as the depiction of ultrasound and magnetic resonance.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) -The advantage of ultrasound is in the absence of radial load on the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)- Compared to other methods, it allows you to more clearly visualize the damage of the joints.
- Arthroscopy-It allows you to determine the damage to the articular cartilage: from the coarse zones (softening of the articular cartilage) with a diameter of less than 10 mm to deep cracks that penetrate up to the underdine bone and the formation of deep ulcers.Surface and medium cracks and surface erosion can also be depicted.
Identification of Coksarrosis usually does not represent specific difficulties, but when evaluating a particular clinical condition, it is necessary to remember the possible secondary origin of the arthritis of the hip joints (as complications of other diseases, for example, with endocrine disorders).
Treatment of hip joints
The treatment of arthritis arthritis can be so conservative (pharmaceutical and non -ascommunications) or functional.Conservative treatment is used in 1-2 stages of the disease, Surgical-at 3 stages.Surgical treatment may be recommended in 2 stages with persistent pain and a lack of reaction to conservative treatment.
The goals of conservative treatment:
- Improvement of quality of life - reduce pain and increase joint mobility.
- Stop or slow down the development of the disease.
Non -treatment methods include:
- Unloading the hip joint (reduction of body weight, the creation of additional support and the transfer of part of the body weight to sugar cane or crutches).
- Physiotherapy Physical Education.
- Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment.
The treatment of the conscientious begins with non -pharmacies, an important role in physiotherapy exercises.With severe pain, the patient should use support.With an intense disease and the presence of contraindications in the endoprotective, support should be used for life.
Pharmaceutical treatment of casteIncludes medicines that reduce the symptoms of the disease.These are analgesic as well as medicines from the Non -Non -Non -NSAID group (NSAID).NSAIDs are divided into non -election and selective.
Analgesics and NSAIDs for articulation of the hip joint are used for a short time to relieve pain and inflammation.Currently, there is no proven advantage of a non -specific anti -inflammatory factor in relation to another, so the choice of a particular drug depends on the side effects and a specific clinical condition caused by it.
We must remember that NSAIDs have some side effects.When you take them, the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum is affected, as a result of which ulcers and bleeding are possible.Some NSAIDs have a toxic effect on the liver and kidneys.In addition, NSAIDs disrupt platelet aggregation and, therefore, the patient is disturbed by thrombosis and there is a tendency to bleed.NSAIDs with prolonged use suppress hematopoiesis processes and can cause aplastic anemia and agriculturalism.NSAIDS selective taking significantly less complications.
Ointments and gels used locally cause fewer side effects than oral products.Heating and pain reduction are used to treat the article.They can contain terrain, menthol, nicotinic acid esters, salicylic, bee poison.Also, NSAIDs have a good effect.
In the absence of the effect of analgesics and NSAIDs or if it is impossible to choose the optimum dose of the drug, the painkillers of the central action can be prescribed in the short term.
In the event of inflammation, endotic administration of corticosteroids is used.Corticosteroids are not used more than 2-3 times a year, as more frequent use can lead to cartilage degeneration.
Medicines that slowly activate the symptoms of the disease include chondroprotective, inappropriate avocado or soy, hyaluronic acid.These drugs are included in the recommendations of the European Antimortic League for the treatment of hip arthritis.Fridays reduce pain and improve joint mobility.
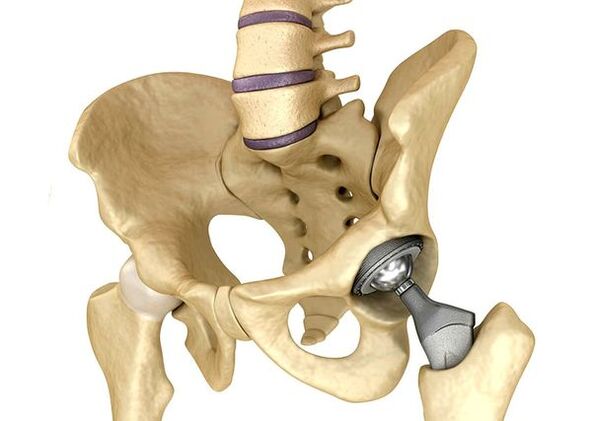
Hip jointsIt is used in severe cases of Stage III, when the pain syndrome cannot be eliminated and joint mobility is significantly limited.The prosthetic hip joint leads to a decrease in pain syndrome, improve the functional state of the joint and the quality of the patient's life.The result remains for 10-15 years, after which a second business may be required.During surgery, hip joint is replaced by artificial imitation of ceramics, metal (more commonly used titanium additions) or polymer.
Forecast.Prevention
The prognosis of hip joint articles in relation to the patient's life is favorable, but the disease often leads to disability.According to the World Health Organization, 80 % of elderly patients with a knife have a breach of mobility and 25 % cannot do daily issues.In this respect, the primary prevention of hip joints is important.
Prevention Measures:

- Reduce body weight.It is necessary to adjust the diet in order to reduce weight and load on the joint.In addition, the decrease in the volume of adipose tissue reduces the amount of inflammation mediators it has released.
- Avoid heavy physical work and overloaded sport.Natural overflows are often the cause of hip joints, while moderate physical activity, on the other hand, improves the condition of the articular cartilage, maintains its normal mobility and reduces the load on other joints.
- Correct the underlying disease.If the patient is detected in diseases that can lead to secondary coksarrosis (endocrine, rheumatic and others), the underlying disease is necessary.The normalization of the hormonal background and the achievement of the persistent recession of rheumatic diseases is also the primary prevention of articulation and allows you to slow down its development.
- Drive a healthy lifestyle.A balanced diet with a sufficient content of vegetable and animal proteins, polyunsaturated fatty acids and limiting simple carbohydrates, as well as moderate physical activity, avoiding the appearance of trim even in the presence of risk factors.
Currently, the prevention of hip joint diseases is mandatory in neonatal and pediatrics.Over time, adapted congenital hip malformation significantly reduces the risk of adulthood.




























